Diabetes is a disease that interferes with the body’s ability to use and store sugar. Too much sugar in the blood can cause damage throughout the body, including the eyes. Diabetic retinopathy is the result of damage to the tiny blood vessels that nourish the retina. It is the leading cause of blindness in the United States. According the the American Optometric Association, a third to half of the people with diabetes don’t receive annual eye exams. In addition, 20-40 percent of individuals with type 2 diabetes have diabetic retinopathy at the time of diagnosis of diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include
- Seeing spots or floaters in your field of vision
- Blurred vision
- Having a dark or empty spot in the center of your vision
- Difficulty seeing well at night
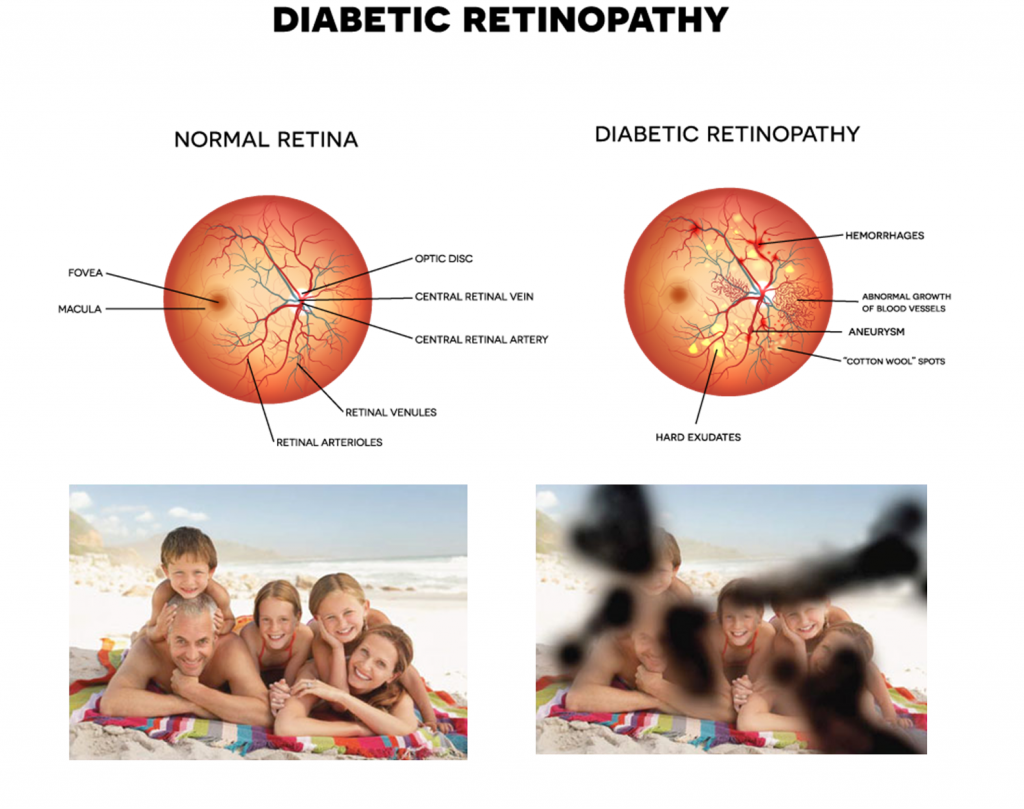
Often there are no visual symptoms in early stages of diabetic retinopathy. That is why it is recommended that everyone with diabetes have a comprehensive eye exam once a year. Early detection and treatment is key to limit vision loss from diabetic retinopathy.
If you are diabetic, you can help prevent or slow the development of diabetic retinopathy by taking your prescribed medication, sticking to your diet, exercise regularly, controlling high blood pressure, and avoiding alcohol and smoking.




